Researchers Reveal Trimethylamine oxide Regulate Fat Deposition in Pigs
According to a study published in Animal nutrition on March 8, a research group led by Prof. YIN Yulong from the Institute of Subtropical Agriculture(ISA)of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), uncovered the effect of trimethylamine oxide (TMAO) on fat accumulation, fatty acid composition, and intestinal microbiota in growing-finishing pigs.
Through extensive analysis, the researchers determined that TMAO supplementation significantly increased microbial overgrowth in the small intestine, especially Escherichia coli. Furthermore, dietary supplementation significantly increased the acetate content in ileum, associated with the abundance of Escherichia-shigella.
In addition, the researchers found that TMAO increased fat deposition in subcutaneous adipose tissue and longissimus dorsi muscle, and decreased fat deposition in liver. TMAO also upregulated the mRNA expression of SREBP1 in C2C12 cell.
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U20A2054), the earmarked fund for China Agriculture Research System (CARS-35), and the Science and Technology Major Project of Yunnan Province (202202AE090032), and Large-scale Healthy Breeding Technology Research and Industrialization Demonstration of pig (202102AE090046).
Contact: Bie Tan
E-mail: bietan@hunau.edu.cn
Hunan Agricultural University
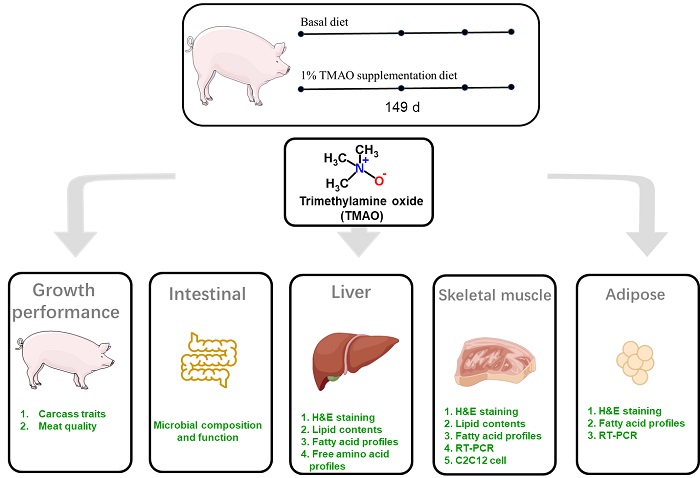
Experimental design. (Image by Zha Andong)
Download attachments: