Did you eat Chinese Guangxi minipig (e.g.Black Small-eared Pig) in your family reunion dinner? If you did, I’m sure it must leave a lasting and pleasant taste in your mouth. Since pigs of this kind are so delicious, researchers want to add their weigh and fat percentage at all times. But how?
Researchers in the Institute of Subtropical Agriculture, Chinese Academy of Sciences (ISA) used soy isoflavones to have a try. Soy isoflavones are constituents of soybeans used widely in human food and livestock nutrition. Their study was conducted to determine the effects of soy isoflavones on changes in body and tissue weight and on insulin-like factor I (IGF-I) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) gene and protein expression in muscle and adipose tissues in Chinese Guangxi minipig.
“In our experiment, a total of 72 male Chinese Guangxi minipigs were fed basal diet (control, Con), low dose of soy isoflavones and high dose of soy isoflavones (HSI)” said researcher LI Fengna in ISA.
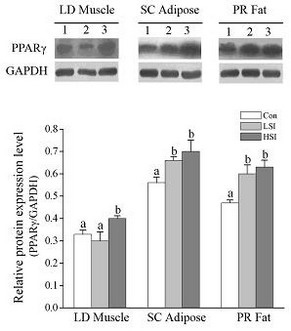
The results showed that HIS increased the body weight (BW) gain and fat percentage of minipigs (P<0.05). In addition, the serum concentrations of IGF-I andinterleukin-6 were increased by high levels of soy isoflavones (P<0.05). Furthermore, a diet containing soy isoflavones enhanced IGF-I mRNA expression levels in longissimus muscle, but decreased these levels in perirenal fat. However, the mRNA and protein expression levels of PPARγ in longissimus muscle and subcutaneous adipose tissue were both increased when compared with the Con. The data indicated that soy isoflavones regulated the BW gain and fat percentage of Chinese Guangxi minipigs, which also showed changes in IGF-I system and PPARγ. “However, we still need to clarify the causative relationship in our further research.” said LI.
This study was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30972118, 31001015), the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation (08JJ3080, 31001015, 31001016 and 31072042), the Major Scientific Projects Foundation of Hunan Province (2009FJ1005) and the State Commission of Science Technology of Guangdong (2006B200330005).
For more information on how to add weight and fat percentage in pigs, please refer to “Regulation of soy isoflavones on weight gain and fat percentage:evaluation in a Chinese Guangxi minipig model”, which was written by LI Fengna, together with her collaborators, and was published on ANIMAL in December, 2011. Details could also be found at
http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=8425606.
|
|
| Figure 1 Effects of soy isoflavones on protein expression levels of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ in muscle and adipose tissue of Chinese Guangxi minipigs fed with a standard diet or with diets supplemented with soy isoflavones. A representative Western blot is shown. (LM = longissimus muscle; SCAT = subcutaneous adipose tissue; PR fat = perirenal fat; 1 = Control (Con); 2 = low dose of soy isoflavones (LSI; 125 mg/kg); 3 = high dose of soy isoflavones (HSI; 500 mg/kg); values with different letters on bars are significantly different (P < 0.05), mean ± s.e. (n = 6 for each group).) |
