IL-15: A Novel Regulator of Obesity in Humans
Obesity is a major public health concern and is increasing at an alarming rate. Approaches for reducing the current obesity epidemic are becoming a primary focus of human healthcare. Traditionally, strategies for treating obesity have mainly focused on dietary and lifestyle modifications such as caloric restriction and increasing physical activity. However, in the long term, it is not an effective treatment strategy for obesity to simply monitoring an individual’s caloric intake and/or activity level. Thus, it is of urgent need to identify effective and novel therapeutics and preventative strategies involved in conquering this disease state.
Recently, a team of researchers from China Agricultural University, the Institute of Subtropical Agriculture, Chinese Academy of Sciences (ISA) highlight Interleukin (IL)-15, a cytokine, as a compound with potential therapeutic value towards obesity and its associated metabolic disorders. IL-15 is expressed broadly by multiple tissues and cell types, indicating a wide range of functions for IL-15 in vivo. Although not widely appreciated, the beneficial effects of IL-15, exogenously delivered or endogenously produced, include increased loss of fat mass and body weight, improved lipid and glucose metabolism, reduced WAT inflammation, enhanced mitochondrial function, alterations in the composition of muscle fibers and gut bacterial, attenuated endoplasmic reticulum stress (Figure 1). However, in contrast to the salutary effects of IL-15 described above, there is evidence showing that IL-15 might promote obesity rather than conferring protection against obesity. Unfortunately, a plausible explanation for these paradoxical findings is lacking, further investigation into the role of IL-15 is thus certainly warranted.
The research was the jointly supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (2013CB127305), the Nature Science Foundation of Hunan Province (S2014J504I), the Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (2016326), the Major Project of Hunan Province (2015NK1002), the Key Project of Research and Development Plan of Hunan Province (2016NK2170), and Youth Innovation Team Project of ISA, CAS (2017QNCXTD_ZCS).
The study entitled “Interleukin-15 in obesity and metabolic dysfunction: current understanding and future perspectives” has been published online in July 2017 of Obesity Reviews, details could be found at http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/obr.12567/full.
Contact: Yin Yulong
E-mail: yinyulong@isa.ac.cn
Institute of Subtropical Agriculture, Chinese Academy of Sciences
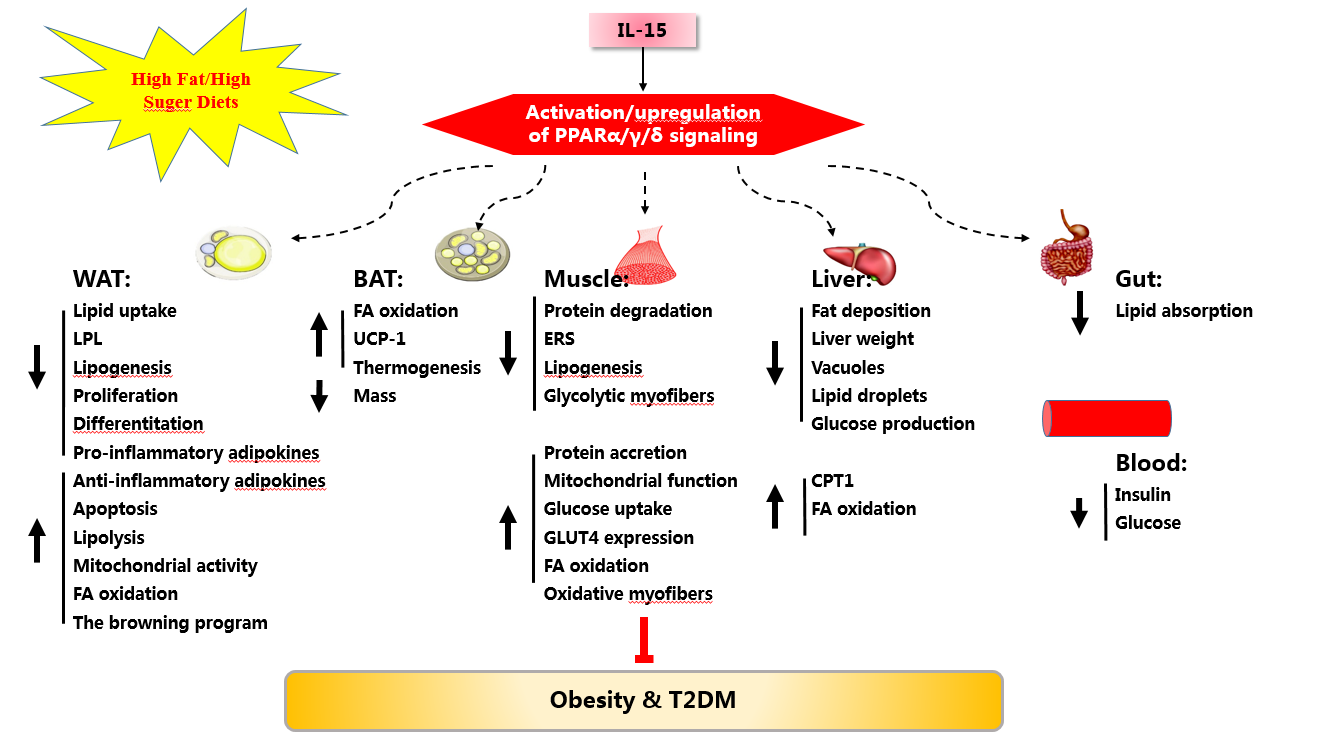
Figure 3. Simplified scheme of possible mechanisms of the beneficial effects of IL-15 treatment on obesity and its related metabolic dysfunction. BAT, brown adipose tissue; CPT-1, carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1; ERS, endoplasmic reticulum stress; FA, fatty acid; GLUT4, glucose transporter 4; IL-15, interleukine-15; LPL, lipoprotein lipase; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; UCP, uncoupling protein; WAT, white adipose tissue.
Download attachments: