Balancing Dietary Amino Acids Contributes to Weight Loss
Increased body fat in humans is closely associated with obesity and diabetes. In swine production, increased body fat is inversely proportional to production efficiency and meat quality. Therefore, a better understanding of fat development is important for both humans and animals.
Branched-chain amino acids (BCAA), containing leucine (Leu), isoleucine (Ile), and valine (Val), can act directly on adipocytes (the major cellular constituent of adipose tissue) to affect fat metabolism, favoring fat reduction. However, the optimal ratio of BCAA is not clear yet.
Recently, researchers from China Agricultural University and the Institute of Subtropical Agriculture (ISA) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences conducted a study to compare and contrast the effects of dietary BCAA ratios on lipid metabolism in different location of adipose tissues and unravel the molecular mechanisms of BCAA ratio action of lipid metabolism.
The researchers found that the optimal ratio of dietary BCAA was within the range of 1:0.75:0.75-1:0.25:0.25. Dietary supplementation with balanced BCAAs could reduce the weight of total fat mass, increase the adiponectin concentration, and modulate adipose tissue function including fatty acid synthesis, transport, and oxidation, as well as lipolysis.
Concomitant with these changes, the phosphorylation of mTOR was decreased, while the AMPKα phosphorylation and the mRNA abundance of PGC-1α and IL-15 were increased in pigs fed diets with balanced BCAA ratios. They suspected that the effects mediated by diets with balanced BCAA ratios were partly mediated by AMPK-mTOR pathway and associated with mitochondrial biogenesis, the AMPK-PGC-1α axis, and IL-15 secreted by muscle tissues (Figure 1).
The research was supported by Nature Science Foundation of Hunan Province, the Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS, the Science and Technology Projects of Hunan Province, the Major Project of Hunan Province, the Key Project of Research and Development Plan of Hunan Province, Youth Innovation Team Project of ISA, CAS, the Earmarked Fund for China Agriculture Research System, and the Plant Germplasm Resources Innovation Project of Strategic Biological Resources Service Network Plan from the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
The study entitled "Branched-chain amino acid ratios modulate lipid metabolism in adipose tissues of growing pigs" was published in Journal of Functional Foods.
Contact: YIN Yulong
E-mail:yinyulong@isa.ac.cn
Institue of Subtropical Agriculture,Chinese Academy of Sciences
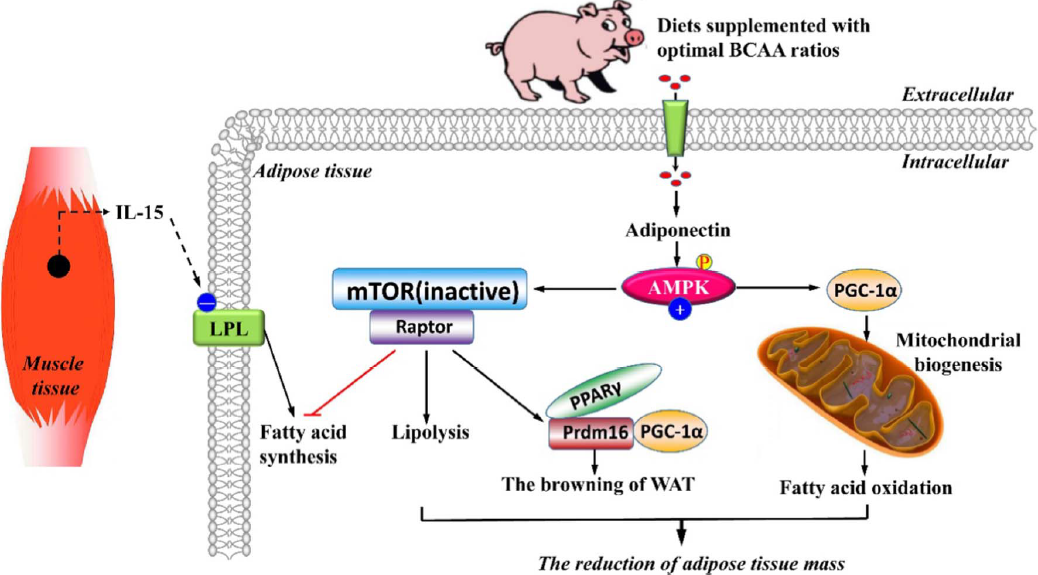
Figure 1: Schematic representation of hypothesized mechanism of BCAA ratio effects on lipid metabolism in adipose tissues of pigs. (Image by ISA)
Download attachments: