Researchers Separated the Key Factors Influencing Runoff and Sediment Yield Changes in Different Karst Watersheds
The ecological environment in karst regions of the Southwest China is fragile and sensitive. For about 510,000 km2 of highly irregularly exposed carbonate rocks in the Southwest karst region are characterized by frequent extreme rainfall, unique hydrogeological structures, shallow and discontinuous soil distribution, complex geomorphic type, and highly heterogeneous landscape. Recently, researchers led by Prof. Kelin WANG from the Institute of Subtropical Agriculture, Chinese Academy of Sciences, demonstrated that the spatial variation and controlling factors of runoff and sediment yield (SY) in different karst watersheds were quantitatively analyzed.
In their latest study published in Water Resources Research on Aug 21, the runoff and SY data of 40 typical karst watersheds in Southwest China from 2009 to 2012 were selected. Altogether, 103 factors of rainfall, lithology, soil, topography and landscape properties were extracted from these different karst watersheds. The complex relationships between runoff, SY and their potential influencing factors was decoupled by partial least squares-structural equation model (PLS-SEM).
The results show that climate, lithology, soil, topography and landscape can explain 79% of runoff variation in different karst watersheds, and 59% of SY variation can be explained by the abovementioned factors. It also indicates that the influence of climatic factors on runoff is significant. Different from runoff, lithology, soil, topography and landscape factors have significant impacts on SY. Landscape factors have the greatest influence on SY.
“Our study confirms the influence of extreme climate on runoff and the influence of landscape on sediment cannot be ignored.” said Prof. Zhenwei Li, the corresponding author of the study. “It will provide scientific basis for soil erosion control and sustainable development of ecological environment in Karst region.”
Contact: Li Zhenwei
E-mail: lizhenwei337@isa.ac.cn
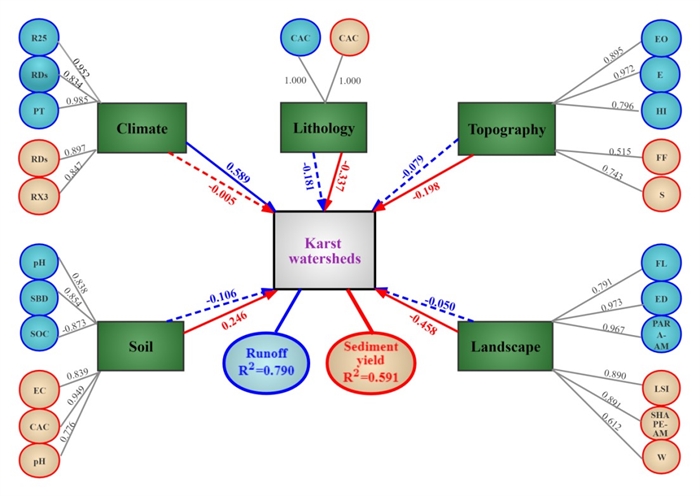
The PLS-SEM analysis of the effects of climate, lithology, soil, topography and landscape on runoff and sediment yield for 40 karst watersheds. (Image by Zhenwei Li)
Download attachments: